The protection and control of utility-scale generation and transformers are critical to ensure the safety and reliability of the power system. These devices are essential components of the electric power grid and require specialized protection schemes to detect and isolate faults.
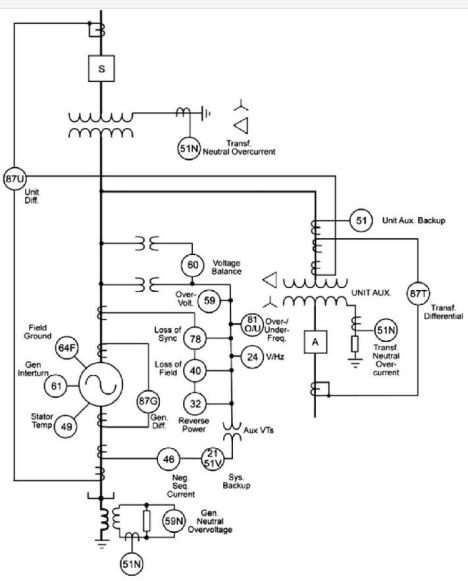
Protection and Control of Utility-Scale Generation
Utility-scale generation refers to large-scale power plants that generate electricity for distribution to the grid. These plants use various types of generators, including synchronous generators, asynchronous generators, and wind turbines, to generate electricity.
The protection of utility-scale generation involves the detection and isolation of faults that may occur in the power system. Faults can occur due to various reasons, including lightning strikes, equipment failure, and human error. The protection system must be able to detect and isolate these faults quickly to minimize damage to the equipment and prevent the power system from collapsing.
One of the critical components of the protection system for utility-scale generation is the generator protection relay. The relay protects the generator against various types of faults, including overvoltage, undervoltage, overcurrent, undercurrent, and loss of excitation.
Another critical component of the protection system is the generator circuit breaker (GCB). The GCB is a specialized switch that disconnects the generator from the grid in the event of a fault. The GCB must be able to operate quickly and reliably to isolate the fault and prevent it from spreading to other parts of the power system.
In addition to the generator protection relay and GCB, other protection devices may be used, including differential relays, distance relays, and directional relays. These devices are designed to detect specific types of faults and respond accordingly.
Protection and Control of Transformers
Transformers are essential components of the power system that are used to transfer electrical energy from one voltage level to another. Transformers can be found at various locations in the power system, including generating stations, substations, and distribution networks.
The protection of transformers involves the detection and isolation of faults that may occur in the transformer or its associated equipment. Faults can occur due to various reasons, including insulation failure, overheating, and overloading.
One of the critical components of the protection system for transformers is the transformer protection relay. The relay is designed to detect various types of faults, including overvoltage, undervoltage, overcurrent, undercurrent, and winding temperature.
Another critical component of the protection system is the transformer differential relay. The differential relay is designed to detect internal faults within the transformer and isolate the faulted section quickly.
In addition to the transformer protection relay and differential relay, other protection devices may be used, including overcurrent relays, under/overfrequency relays, and overvoltage relays. These devices are designed to detect specific types of faults and respond accordingly.
Conclusion
The protection and control of utility-scale generation and transformers are critical to ensure the safety and reliability of the power system. These devices are essential components of the power system and require specialized protection schemes to detect and isolate faults. The protection system must be able to detect and isolate faults quickly to minimize damage to the equipment and prevent the power system from collapsing. Proper protection and control schemes are necessary to ensure the reliable and safe operation of the power system