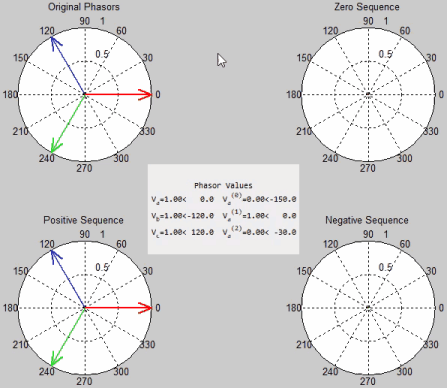
Symmetrical components is a powerful technique used in electrical engineering to analyze and understand unbalanced conditions in three-phase power systems. In a balanced three-phase system, the voltages and currents have equal magnitudes and a phase difference of 120 degrees. However, in real world scenarios, imbalances can occur due to various factors such as faults, unbalanced loads, or system asymmetry.
Symmetrical components allow us to break down an unbalanced system into a set of balanced components called positive sequence, negative sequence, and zero sequence components. These components simplify the analysis and provide valuable insights into the system behavior.
- Positive Sequence Component: The positive sequence component represents the balanced part of the system. It has the same magnitude and phase as the original system and is responsible for normal operation. It is denoted by the subscript “1”.
- Negative Sequence Component: The negative sequence component represents the unbalanced part of the system where the currents and voltages have equal magnitudes but are displaced by 120 degrees. It is caused by imbalances in the system and can lead to issues like overheating of equipment. It is denoted by the subscript “2”.
- Zero Sequence Component: The zero sequence component represents the unbalanced part of the system where the currents and voltages have zero phase displacement. It arises from ground faults or imbalances in the system. It is denoted by the subscript “0”.
By breaking down the system into these components, engineers can analyze the effects of unbalanced conditions on power flow, voltage regulation, and protection schemes. The symmetrical components technique helps identify the causes of unbalance and design appropriate mitigation measures.
Additionally, symmetrical components are used to develop protective relaying schemes that can detect and respond to faults in a power system. By analyzing the symmetrical components of fault currents, relays can accurately determine the type and location of a fault, enabling prompt protective actions.
Overall, symmetrical components provide a systematic approach to understand and mitigate the effects of unbalanced conditions in electrical power systems, ensuring reliable and efficient operation.